(ICIP2017)SIMPLE ONLINE AND REALTIME TRACKING WITH A DEEP ASSOCIATION METRIC
主要贡献
Simple Online and Realtime Tracking (SORT)
-
集成外表信息来提升SORT的性能
integrate appearance information to improve the performance of SORT
-
可以追踪被产时间遮挡的目标,减少 ID switch
we are able to track objects through longer periods of occlusions, effectively reducing the number of identity switches
-
在大的人物re id 数据集上训练相关矩阵
we place much of the computational complexity into an offline pre-training stage where we learn a deep association metric on a largescale person re-identification dataset.
-
使用 measurement-to-track associations 在视觉空间内进行最邻近查询
we establish measurement-to-track associations using nearest neighbor queries in visual appearance space.
-
减少了45%的 ID switch
简介
tracking-by-detection has become the leading paradigm in multiple object tracking.
物体的轨迹被认为是全局最优化的问题
object trajectories are usually found in a global optimization problem that processes entire video batches at once.
基于batch processing 的方法无法实现在线应用
due to batch processing, these methods are not applicable in online scenarios where a target identity must be available at each time step.
Simple online and realtime tracking (SORT)
简单的SORT 是基于图片空间的卡尔曼滤波(Kalman filtering in image space and) 并利用匈牙利算法进行逐帧数据结合(frame-by-frame data association using the Hungarian method with an association metric that measures bounding box overlap.)用关联矩阵来评估bbox的重叠率。
SORT会引入大量的ID switch, 因为关联矩阵只有在状态评估置信度高的情况下才准确。
SORT 不能很好地处理遮挡问题。
为了解决此问题,本文将运动和外观信息引入矩阵,
使用在大尺度行人 re id 数据集上训练的CNN
利用深度关联矩阵来SORT(SORT WITH DEEP ASSOCIATION METRIC)
利用卡尔曼滤波和逐帧数据融合。
追踪句柄与状态估计
The track handling and Kalman filtering framework is mostly identical to the original formulation in [12].
使用标准的卡尔曼滤波和线性观测模型
We use a standard Kalman filter with constant velocity motion and linear observation model,
$(u,v,\gamma,h, \dot{u}, \dot{v}, \dot{\gamma},\dot{h})$ 8维向量来表示跟踪目标的状态,bbox中心坐标,宽高比,高度,及其对应的速度。
$(u,v,\gamma,h)$ 为目标状态的直接观测值。
计数器会累积每一个track自最后一次被匹配所经历的帧数,超过阈值则删除。
对于每一帧,如果存在没有被匹配的bbox,则会分配新的track
每个新track会有3帧的考核期,不满足考核则会被删除。
During this time, we expect a successful measurement association at each time step. Tracks that are not successfully associated to a measurement within their first three frames are deleted.
匹配问题
A conventional way to solve the association between the predicted Kalman states and newly arrived measurements is to build an assignment problem that can be solved using the Hungarian algorithm.
传统思路是利用匈牙利算法将根据卡尔曼滤波预测的数据与当前帧实际检测的数据进行匹配。
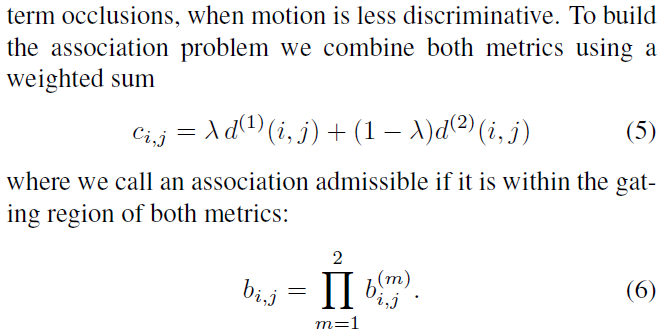
结合运动和外观信息。
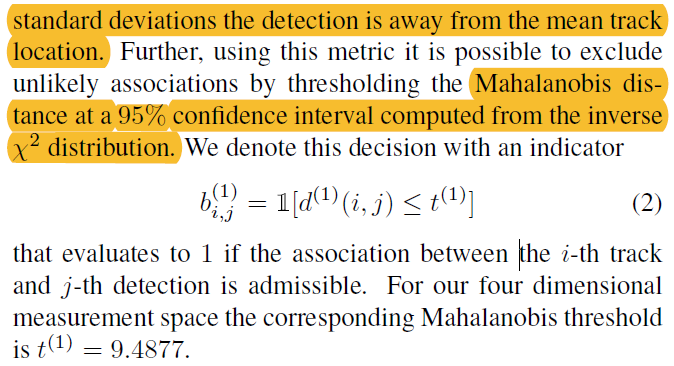
使用马氏距离(马哈拉诺比斯距离)来计算卡尔曼算法预测的状态与当前检测的状态之间的距离
Mahalanobis distance between predicted Kalman states and newly arrived measurements:

马氏距离将状态预测的不确定性转化为评估检测值与历史值之间的标准差
The Mahalanobis distance takes state estimation uncertainty into account by measuring how many standard deviations the detection is away from the mean track location.
利用0.95的置信区间可以排除不相似的匹配
马氏距离仅适用于运动不确定性低的问题,但是通过卡尔曼算法预测的目标的位置是十分模糊的。相机的移动也会带来图片极大的位移。
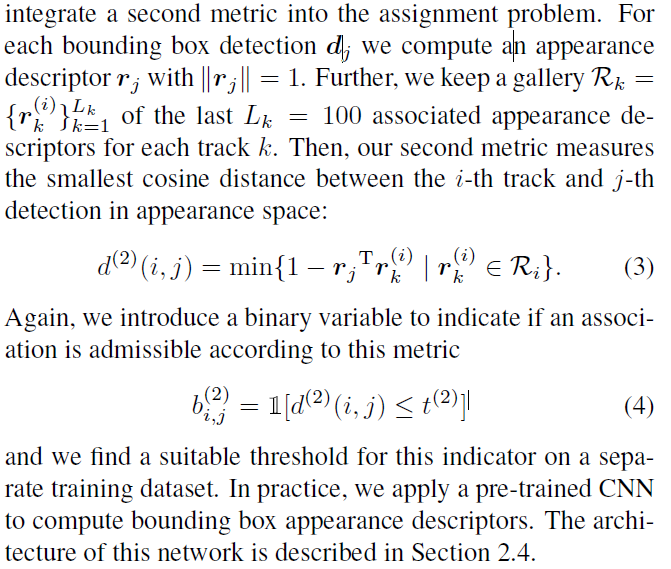
所以引入外观描述,对于每个track会记录100个外观历史,计算两者之间的最小距离
两个矩阵独立运作互相补足。马氏距离通过评估位移,适用于短时追踪,而外观信息则有利于长时间遮挡后的追踪恢复。
匹配级联
采用子问题级联的方式来解决匹配问题
Instead of solving for measurement-to-track associations in a global assignment problem, we introduce a cascade that solves a series of subproblems.
如果物体被长时间遮挡,卡尔曼滤波预测将会不准确。

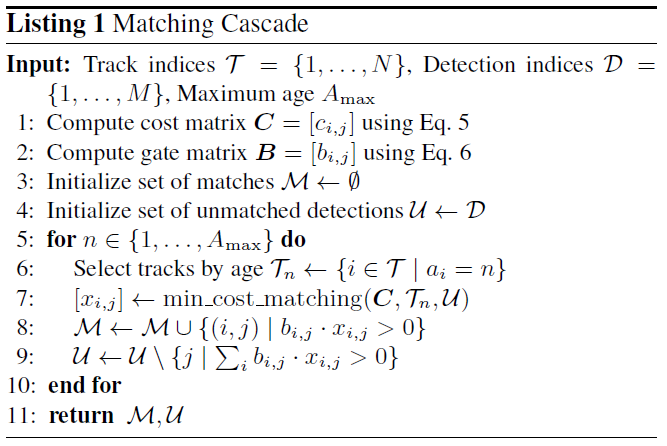
对于age较小的track会优先匹配

最后一次循环在剩余的track和detectin中进行一次传统的sort匹配
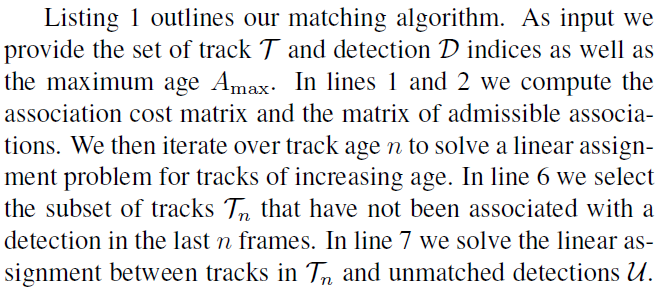
深度外观描述器
使用最邻近查询而不采用额外的矩阵学习依靠着良好预训练的特征提取网络。

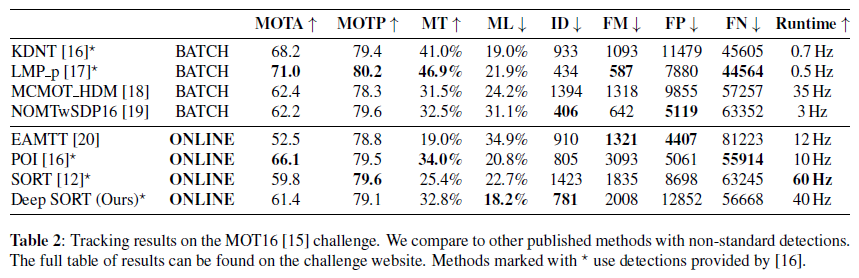
实验
使用Faster-RCNN作为输入
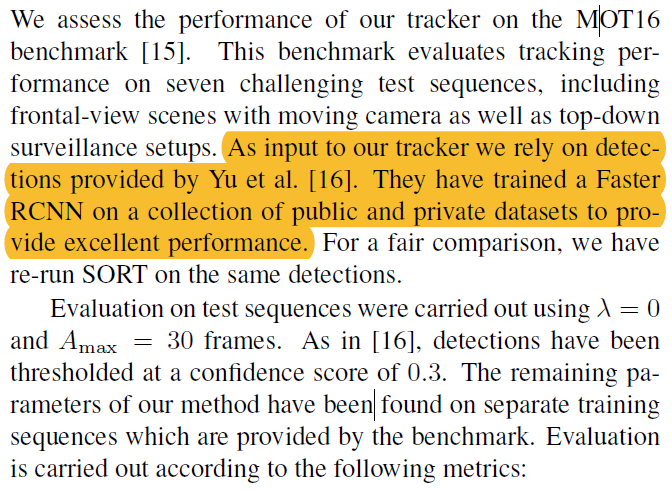
-
Previous
MOTS: Multi-object tracking and segmentation -
Next
(CVPR2020)Learning a Neural Solver for Multiple Object Tracking
本文浏览量: 次